A grader is an engineering machine primarily used for leveling land, scraping soil, and finishing roads. It achieves efficient earthwork operations through an adjustable blade and is commonly seen in the construction and road building sectors
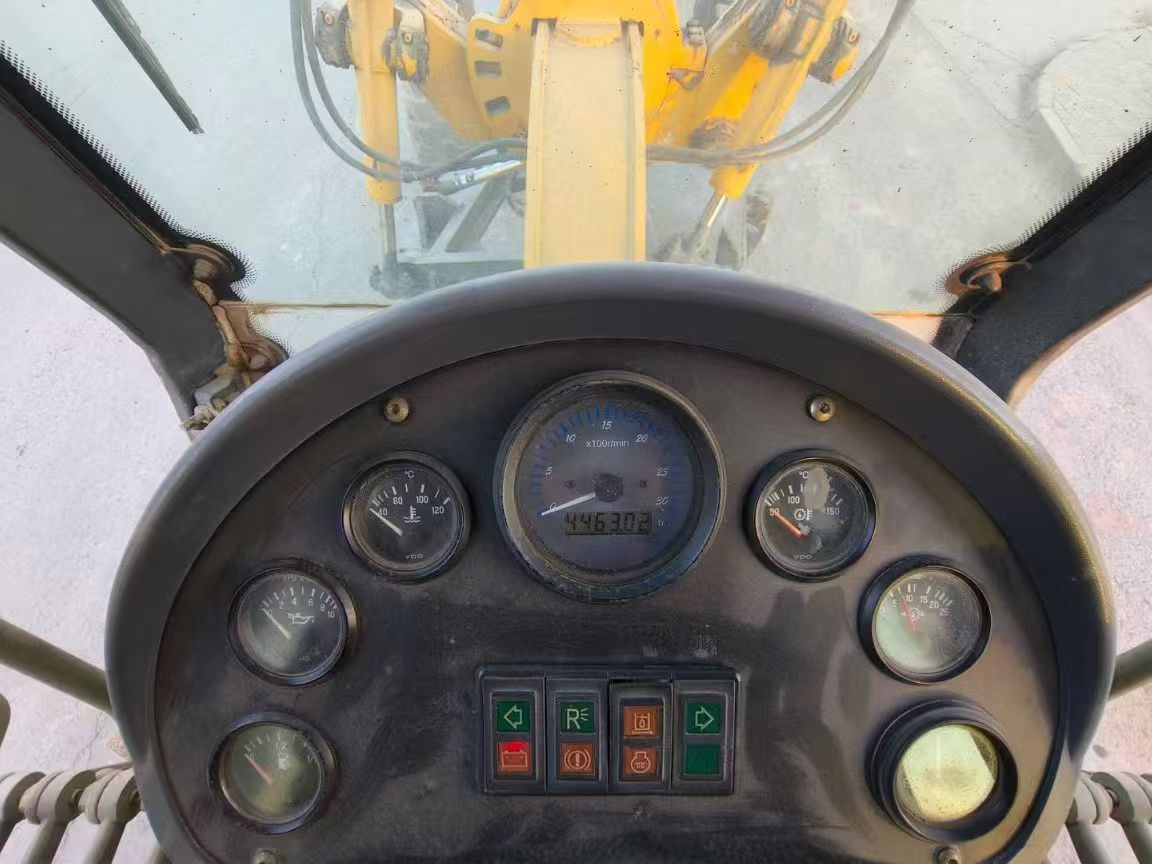
June 2014 production, operating hours 4463. Daily maintenance during use was meticulous, full body original factory paint. Engine cold starts smoothly, idles steadily without abnormal noises. Transmission shifts smoothly, steering is precise, controls respond sensitively, braking distance is short! Truly an excellent used motor grader, high cost-performance ratio!
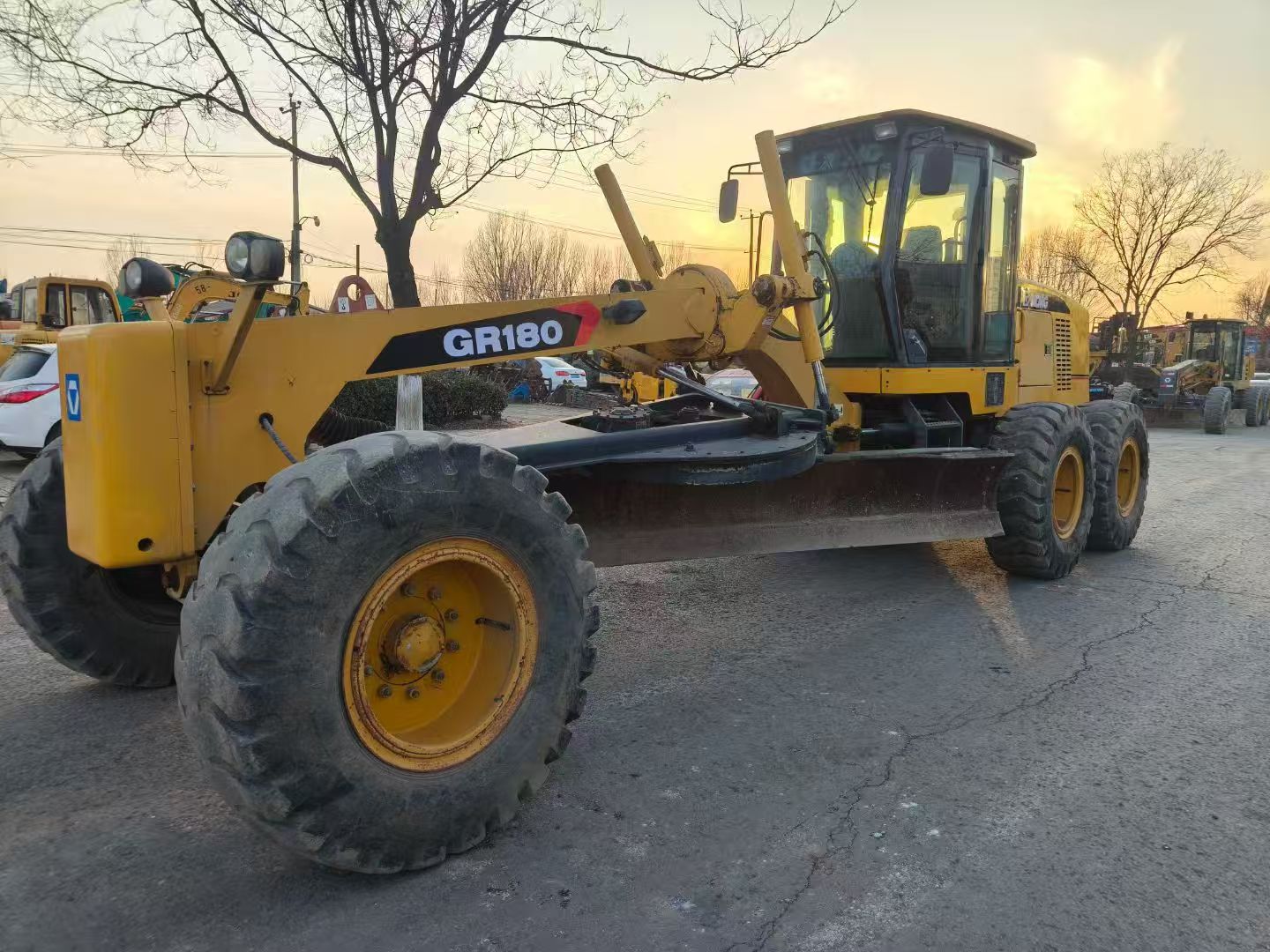

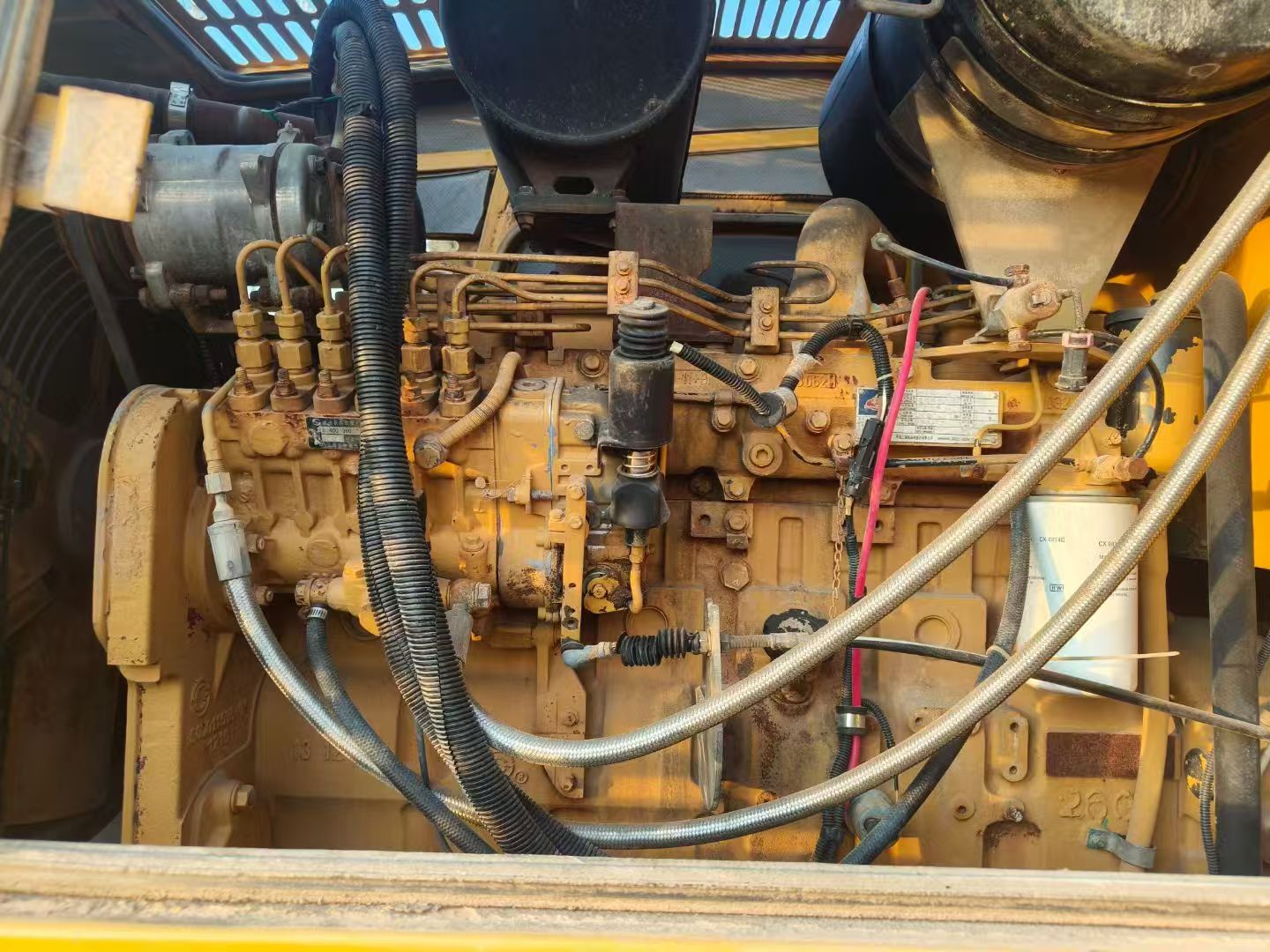
The GR180III motor grader is equipped with a Shangchai SC8DK280G3 high-efficiency diesel engine, delivering ample traction and operational efficiency. Its optimized hydraulic system, combined with electronic control handles, enables precise multi-angle adjustments including ±90° rotation, side-shift, and tilt of the scraper blade. The wide blade design enhances leveling productivity, while the heavy-duty chassis and articulated steering ensure stability in complex working conditions. The spacious cab, panoramic visibility, and vibration-damping features significantly reduce operator fatigue.
XCMG GR180III Detailed Specifications
Model: GR180III
Operating Weight: 16,800 kg
Overall Dimensions (L×W×H): 9.65 × 2.55 × 3.35 m
Wheelbase: 6.2 m
Engine Model: Shangchai SC8DK280G3 (China III Emission)
Rated Power: 209 kW / 2200 rpm
Max. Torque: 1,080 N·m / 1,500 rpm
Fuel Tank Capacity: 290 L
Moldboard Dimensions (L×H×T): 4,000 × 610 × 25 mm
Moldboard Side Shift: Left 1,050 mm / Right 800 mm
Max. Cutting Depth: 500 mm
Moldboard Lift Height: 450 mm
Transmission: Torque Converter + 6F/3R Fixed-Shaft
Drive Type: All-wheel drive (6×4)
Min. Turning Radius (Front Wheel Center): 8.2 m
Tire Specification: 17.5-25 (Ply Rating 28PR)

Daily Maintenance for Motor Grader
1. Fluid Level Check: Check engine oil, hydraulic oil, and coolant levels daily; replenish promptly. Replace hydraulic oil every 250 hours.
2. Cleaning Maintenance: Clean mud from the machine body after operation; focus on cleaning the radiator and air filter. Check tire pressure and blade wear.
3. Lubrication Maintenance: Apply lithium-based grease daily to moving parts like blade hinges and bearings.
4. Function Test: Check lights, brakes, and hydraulic system response before startup; observe dashboard warning lights after operation.
5. Safety & Records: Shut down and disconnect power during maintenance; record operation logs (anomalies, fuel consumption). Increase cleaning/lubrication frequency in harsh environments.
Core Objective: Prevent failures, extend service life, ensure operational safety.